& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Industrial design software helps users create, analyze, visualize, and communicate design intent and aesthetics before building a physical prototype. Many everyday products, from tablets to headphones to cars, have been designed using industrial design software.
Designers can accelerate their process with full-featured industrial design software that includes computer-aided design (CAD) abilities for 2D concept sketching and precise 3D modeling. Software simulation functions can conduct virtual tests of a product design’s physical characteristics and performance. Meanwhile, robust visualization features should include high-quality rendering for producing lifelike, interactive graphic and animated representations of the product for design reviews on computer, mobile, or extended reality (XR) devices.
At the core of industrial design lie the principles of form and function. The designer must balance the imperatives of appealing aesthetics—the product’s contours, colors, and materials—with functionality, including features, ergonomics, and usability.
Those are the tried-and-true industrial design principles, but other modern principles have also asserted their importance. For instance, design for manufacturing (DfM) prioritizes a product’s materials, dimensions, and other design aspects to align with specific production processes like 3D printing, CNC machining, injection molding, or others. Sustainability is another fundamental principle that guides designers to choose energy-efficient manufacturing processes, eco-friendly materials, and recycling or responsible disposal methods for the end of the product’s lifecycle.
There are many types of industrial design, from broad, general categories to specific disciplines. On the more general side, product design is the pursuit of designing physical products from concept to production for functionality, aesthetics, and user-friendliness.
Some more specific areas include furniture design, which balances form and function with comfort and durability; consumer electronics design, which considers the latest technological trends and features; and automotive design, which adds heightened concern for safety and aerodynamics into the mix. Medical device design is also highly concerned with safety so that surgical devices, implants, prosthetics, and other tools are medically effective and reliable. Packaging design balances the need to protect the product while appealing to and informing the customer.
Some types of industrial design apply to nearly any kind of product. For example, sustainable design considers factors such as energy use, materials, waste, and product lifecycle to be environmentally and socially responsible. Also, inclusive design—sometimes called universal design—applies to products, services, and spaces designed to be accessible to as many people as possible, regardless of differences in ability, language, age, gender, culture, or any other quality.
Learn some of the top benefits of industrial design software from Autodesk.
With industrial design software, designers have an immersive and intuitive 3D space to efficiently explore innovative ideas. Though the software accurately depicts designs, designers can experiment with creative product development.
Besides 3D modeling, industrial design software provides full visualization functions, including high-quality rendering and realistic animations for presenting designs to clients and stakeholders with a lifelike feel. Effectively communicating early concepts and design intent with visualization helps teams make important design changes before prototyping and production.
Cloud-connected industrial design software allows engineers, designers, manufacturers, marketers, clients, and other stakeholders to share files and collaborate in real-time from any location. Collaboration features such as multi-user editing, commenting tools, and version control can speed up the design process and lead to better results.
Learn more about the different types of 3D modeling used in industrial design software.
Polygonal modeling software is used in industrial design for concept modeling and is helpful for quick ideation.
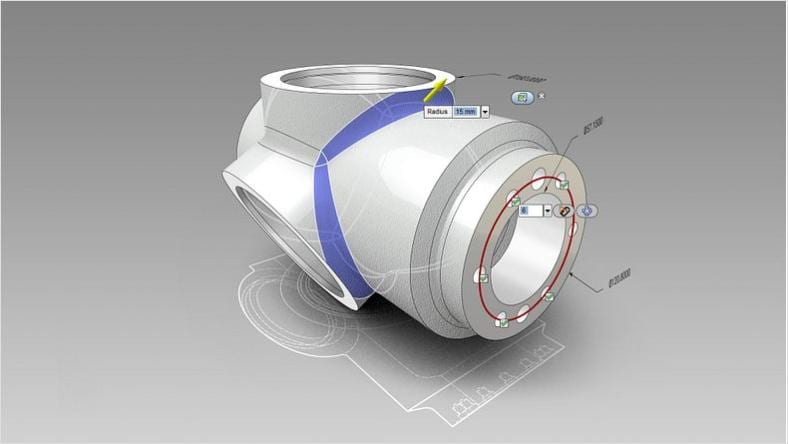
Surface modeling software is used widely across industrial design and lets designers create controlled class A surfaces and adjust the curvature continuity of freeform 3D surfaces with high precision.
Solid modeling creates 3D models, assemblies, and drawings for industrial design projects.
With parametric modeling in industrial design software, you can change parameters, altering the shape of the design based on those values
Image by Jinda/iStock/Getty Images
Professional-grade product design and engineering tools for 3D mechanical design, simulation, visualization, and documentation.
Industrial design software to sketch, concept model, surface, and visualize. Available as Alias Concept, Surface, and AutoStudio.
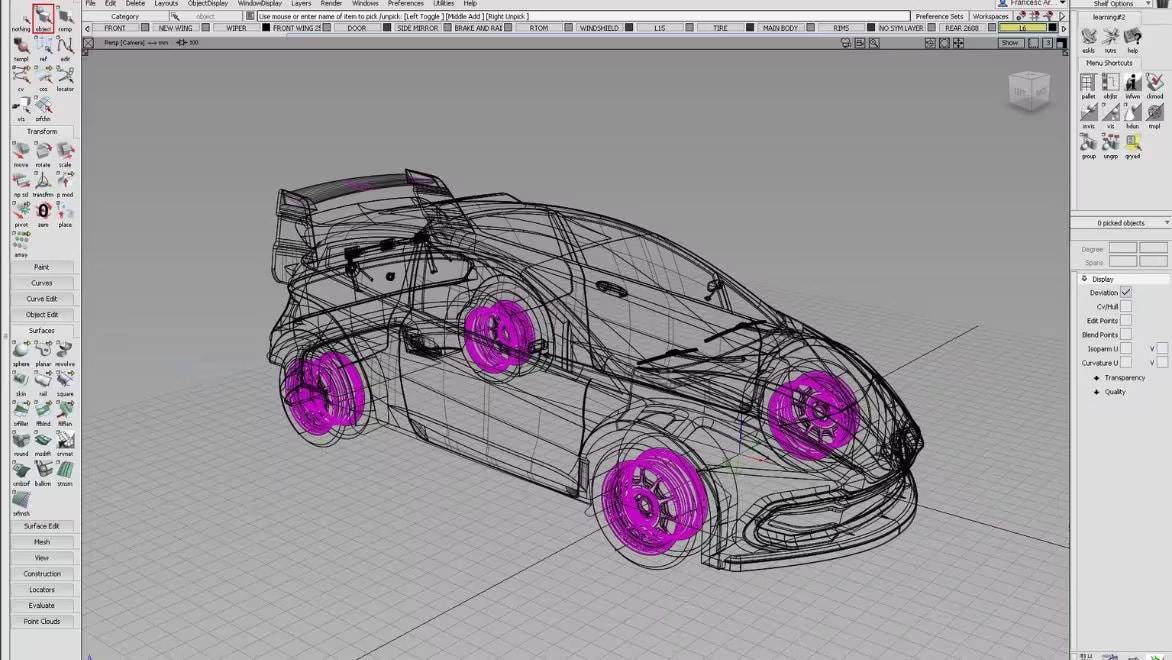
3D virtual prototyping software for automotive design—available as VRED Design, VRED Professional, and VRED Presenter
Discover how Autodesk customers use industrial design software in their projects.
CIXA DESIGN
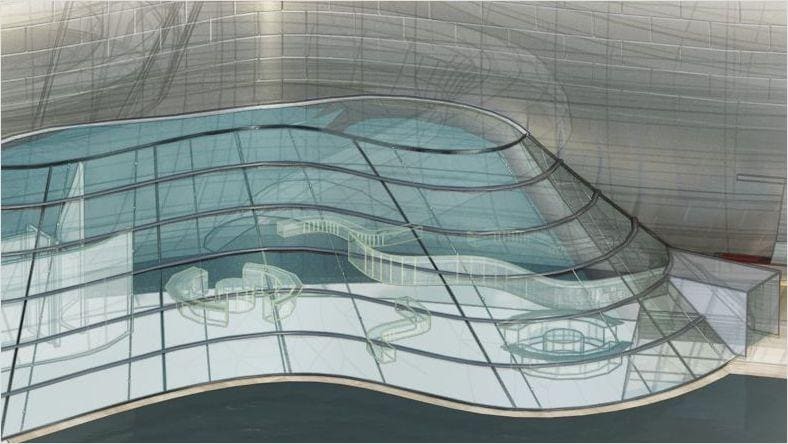
This Spanish automotive design firm rethinks the image of electric cars, and by fully digitalizing its operations with Autodesk Alias and VRED, its resource management has become more sustainable.
Image courtesy of Design Consulting
LIMBFORGE
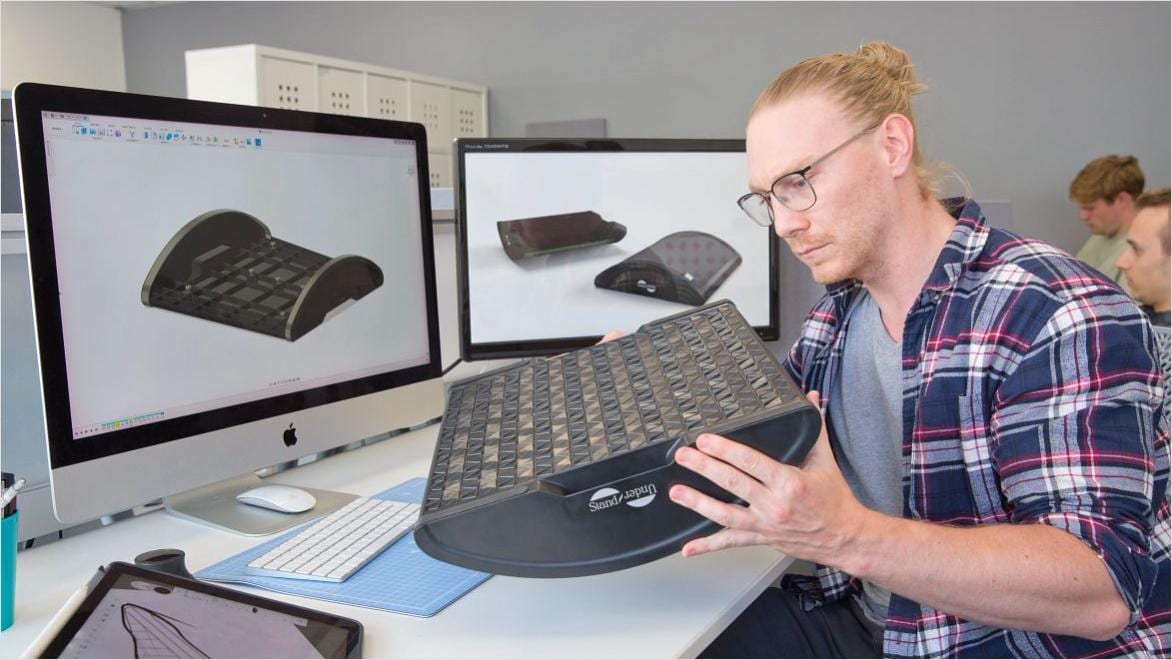
LimbForge designs 3D-printable prosthetics customized for individuals and the cultural contexts of developing countries. The nonprofit benefits from Fusion’s integrated CAD/CAM capabilities as it develops its own software using Autodesk Forge.
Image courtesy of LimbForge
ITERATE DESIGN AND INNOVATION
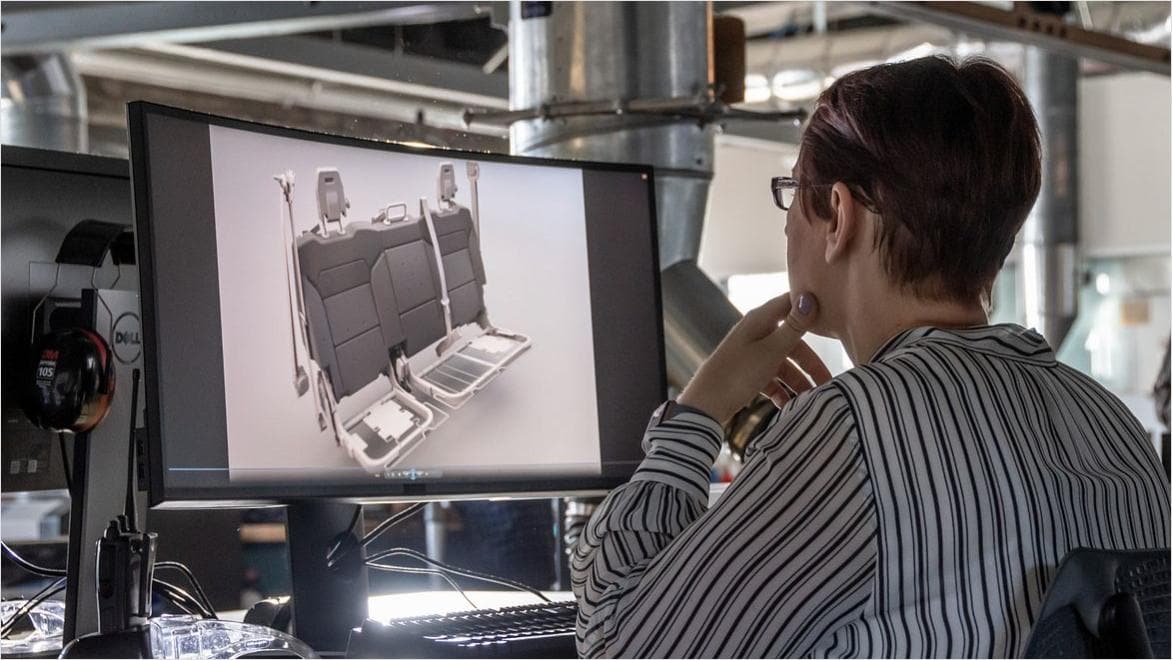
The small team at ITERATE uses its industrial design expertise to help startups bring their innovations to life quickly, designing products in Fusion that the startups can market or use to secure funding.
Photo courtesy of Iterate UK
BLUE PROJECTS
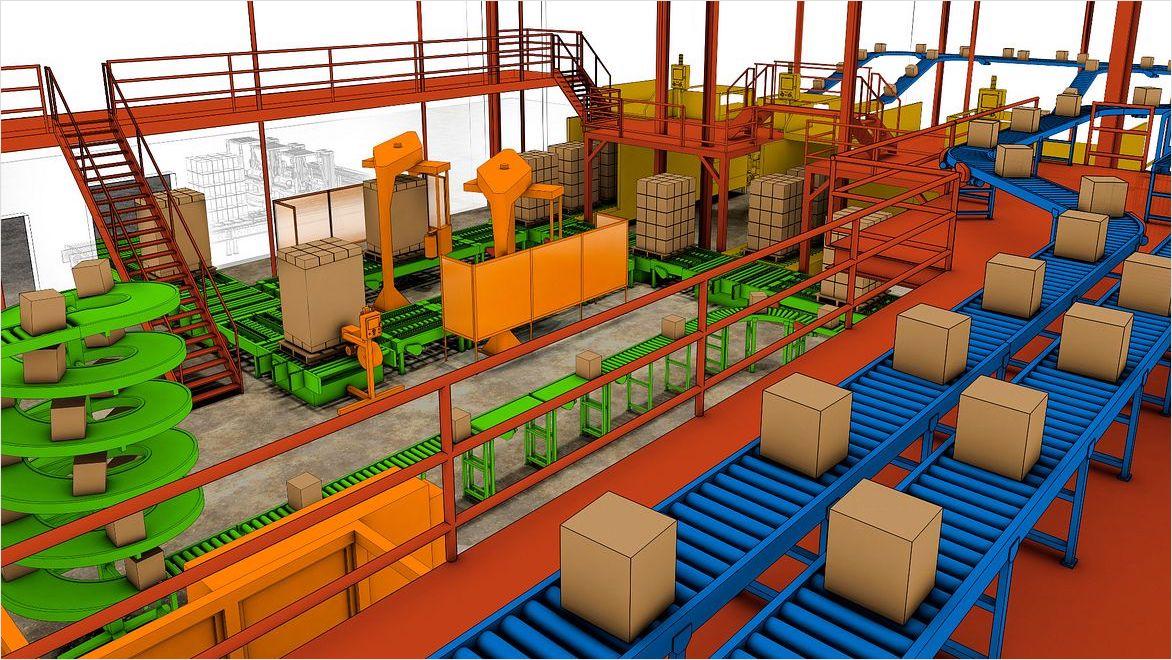
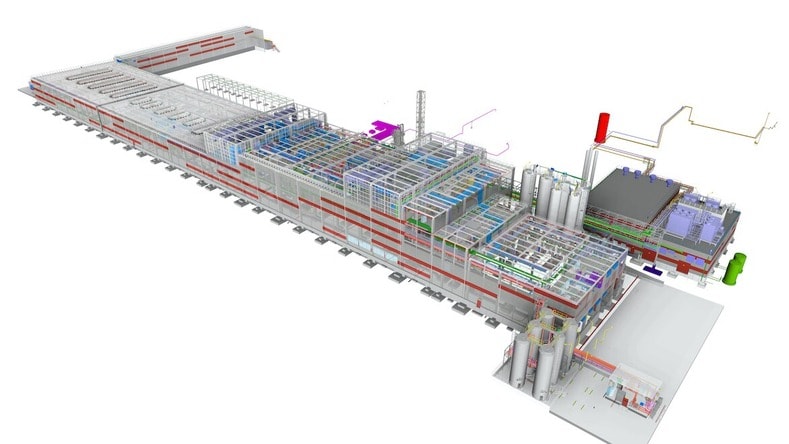
This global manufacturing and logistics facilities firm combines BIM and digital factory planning to represent a building or production equipment digitally, streamlining the data input from several Autodesk software products.
Image courtesy of Blue Projects
Learn more about industrial design with these helpful resources from Autodesk.
Learn how industrial design differs from engineering and what industrial designers do with specific examples of products they make and the software they use.
With early sketches, industrial designers work out initial ideas and visualize product details. Read more about the process and the industrial design software that transforms sketches into 3D models.
This Autodesk University class shows industrial designers how and why they can use Fusion software simulation to perform finite element analysis (FEA) on designs and export simulation reports for engineering.
See how Autodesk Alias streamlines industrial design processes like concept modeling and detailed surface modeling.
With remote work here to stay, industrial designers likely face a hybrid future of working in person and remotely while maintaining dynamic collaboration through cloud-connected software like Autodesk Fusion.
Industrial design software of the near future will unleash creative potential through machine learning, templates, and open sourcing—according to this Autodesk University session.
Industrial design software is important for designers for many reasons. The software’s streamlined workflow automates many manual, repetitive tasks and provides the highest level of precision compared to hand drawings. With cloud-connected industrial design software, designers can easily share their files and data, making collaboration easy among team members and stakeholders.
The software’s high-level functions for simulation and visualization also help designers simulate stress tests of the products in real-world conditions and render highly realistic interactive graphics and animations for lifelike design reviews.
Key features to look for in industrial design software include comprehensive sketching, modeling, and editing tools for 2D and 3D designs. Collaboration and sharing features are also crucial, including multi-user editing, version control, and cloud-connected file and data sharing.
Going deeper, industrial design software should have simulation capabilities so designers can test and optimize their creations and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) before prototyping. When it’s time to make a prototype or even a finished product, industrial design software should have computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) features such as creating manufacturing drawings and sending the design to a 3D printer or a CNC machine.
Industrial design software streamlines the design process by automating repetitive tasks and decreasing errors through accurate operations. Cloud-connected industrial design software also makes it easier and faster to share data with anyone in the world and collaborate with engineers, manufacturers, marketers, clients, and even customers.
The software facilitates rapid prototyping, especially if it integrates CAM functions like Autodesk Fusion. With built-in testing and simulation features, industrial design software can identify product performance so designers can make critical adjustments before producing physical prototypes, saving time and cost.
While industrial designers have a highly creative profession, they face many challenges and have to work within significant constraints, which can limit imagination. First, they must balance form and function; designs should look attractive while also ensuring a good, functional user experience. This design constraint also involves understanding user expectations and needs and keeping up with and anticipating shifts in market demand.
Designers also face time and cost constraints depending on the budget and deadlines for a project. They have to consider the manufacturability of designs, quality control, and compliance with product regulations and standards. Product sustainability also influences decisions regarding product materials, lifespan, manufacturing methods, and disposal or end of life.
The system requirements for running industrial design software with 3D modeling, simulation, and rendering capabilities are an important consideration but don’t require a high-end computer. As usual, the recommended system specs for the smoothest performance are higher than the minimum requirements.
Industrial design software typically runs on the Windows, with some programs running on MacOS or even Linux. A decent processor (CPU) is needed, with an Intel i5, i7, or higher (or the AMD equivalent) recommended. The computer should also have a dedicated graphics card (GPU) for handling rendering and complex 3D models.
A solid-state drive (SSD) is better than a hard disk drive (HDD) because of its faster file saving and data loading.
Yes, industrial design software assists in prototyping and design concept testing. This type of software makes iterative design faster and enables rapid prototyping by integrating with techniques such as 3D printing.
If the software includes simulation features, it could test for things like distribution, heat transfer, and fluid dynamics without producing a physical prototype first. Industrial design software’s visualization capabilities have realistic renderings and animations of a product, making design reviews among team members, clients, and stakeholders possible from remote locations and productive without needing a physical prototype.
The terms “CAD software” and “industrial design software” are sometimes used interchangeably, but there are differences.
Both types of software offer 3D modeling for product development. However, CAD software is more technical and focused on the engineering and manufacturing aspects of creating precise models of physical components. It may include simulationfeatures for predicting the computational fluid dynamics, thermal characteristics, and other types of performance of the physical part.
Meanwhile, industrial design software is usually more conceptual and artistic, focused on the product model’s ergonomics, aesthetics, and usability. It may include extra features for more detailed surface modeling, material selection, visualization, and animation.
Some software, such as Autodesk Fusion , integrates a comprehensive 3D product design and development feature set that would qualify it both as CAD software and industrial design software.